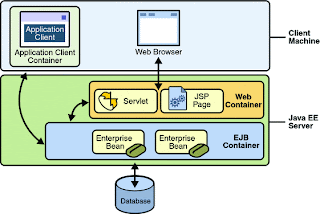
- web tier
- better support for web service
- modern way for developing dynamic web pages
- business tier
- easier way to writing Enterprise Java Bean
- more to declaration than code-oriented
- servlet
- server-side programming written in java
- runs inside servlet container
- advantages
- multithreaded
- stable environment and easy to deploy
- inherits all good features of java programming language
- lifecycle
- 3 phases :
- initialization
- service client request
- destruction
- java server pages (JSP)
- offer layer of abstraction on top of the server
- easier to code than servlet but less control
- just like high programming language and machine language
- element :
- directives - instruction to JSP container
- 3 main destructives : page, include and taglib
- comments
- HTML comment - content visible to end user in the web browser
- JSP comment - not visible to end user
- scripting element - the area where the main java code reside
- 3 categories
- expression - accessing the value of java variables
- scriptlet - one or more java statement in a JSP page
- declaration
- action
- templates
- java bean
- self-contained java class
- provide set and get methods for accessing and updating its attributes from other classes
- jsp implicit object
- request
- read the values of the HTML form in JSP, received as part of HTTP request sent by the client to the server
- response
- sent necessary information from the server to the client
- pageContext
- to get any attributes from any scopes
- session
- application
- put load on JSP container
- out
- send HTML content to web browser
- session
- small and temporarily unique connection between server and a user enabling it to identify that user across multiple pages request or visit that site
- session management
- what ?
- to use API provided by application server to identify the user across multiple page request
- why ?
- hundreds and thousand simultaneous user can be visiting your site and if you can identify each of them separately then it can provides tremendous benefits
- uses
- customization
- to show different view of your websites
- to show differnt content depending on user preferences
- security
- allow membership based access to the site
- after log in, you can identify member from non-member by setting an attributes on the user session to some value
- user behaviour
- log user view like how many ad views have been show to user
- no response shown in the lot, then its time to change the ad
- techniques
- url rewriting
- another way of to support anonymous session tracking
- cookies
- JSP and JDBC
- built in support for databases processing
- provides set of clasess and interfaces that allow java application to work with RDBMS
- MVC
- model - manages the behavior and data of the application domain, responses to request for information about its state ( from view ), and response to instruction to change state ( from controller )
- view - renders the model into a form suitable for interaction
- controller - receives user input and initiates a response by making calls on model objects
- MVC Architecture
- dividing application component into three different categories : Model , View , Controller
- its component has unique responsibility and each of them independent to other component
- changes in one component has no or less impact on other component
- Model
- responsible for providing the data from the database and saving the data into the data store
- all business logic are implement in the Model
- sata access, data validating and data saving logic are part of the model
- View
- represent user view of the application
- Controller
- intermediary between model and view
- responsible receiving request from client
- one request is received from client executes appropriate business logic from the model and produces output to the user using view component
- apache struts
- struts frame work is the implementing MVC design pattern for the JSP
- provide three key component :
- request - provide by the application developer that is use to mapped to a particular URI
- response - used to transfer control to other resource which will be responsible for completing the response
- tag library - helps the developer to creates interactive form based applications with server pages
- struts workflow
- JSF
- easy to build user interfaces for java web application by assembling reusable component in a page
- is a vent driven
- based on MVC design pattern
- benefits :
- provides many tag library for accessing and manipulating the components
- automatically saves the form data and repopulates the form when it is display at client side
- is a specification and vendors can develop the implementation for JSF
- encapsulate the event handling and component rendering logic from programmer
Tuesday, 1 January 2013
java web technologies...
communication of java EE :
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)

No comments:
Post a Comment